The RSA Conference is the largest cybersecurity conference in the United States. Approximately 45,000 people attend RSA each year. CU*Answers attends each year to learn the latest trends in cybersecurity technology, attack vectors, and compliance. In this series, we summarize what we learned to help our network remain current regarding cybersecurity events and report confidently to their boards, members, and examiners. This article discusses how cybercriminals are organized, and how cybercriminal gangs operate as big business.
Modern cybercrime is organized as a business. Over the past fifteen years cybercrime developed from isolated groups of individuals (where personal ego was often the most important motivator) to highly organized crime gangs where greed is the primary stimulus for much of the organization. While politics or revenge can be a motivator for the top of the cybercrime syndicate, money is the key lure. Although FBI law enforcement has had some success in tracking down and extraditing foreign hackers to the United States, the cybercrime business has proven to be both resilient and growing.
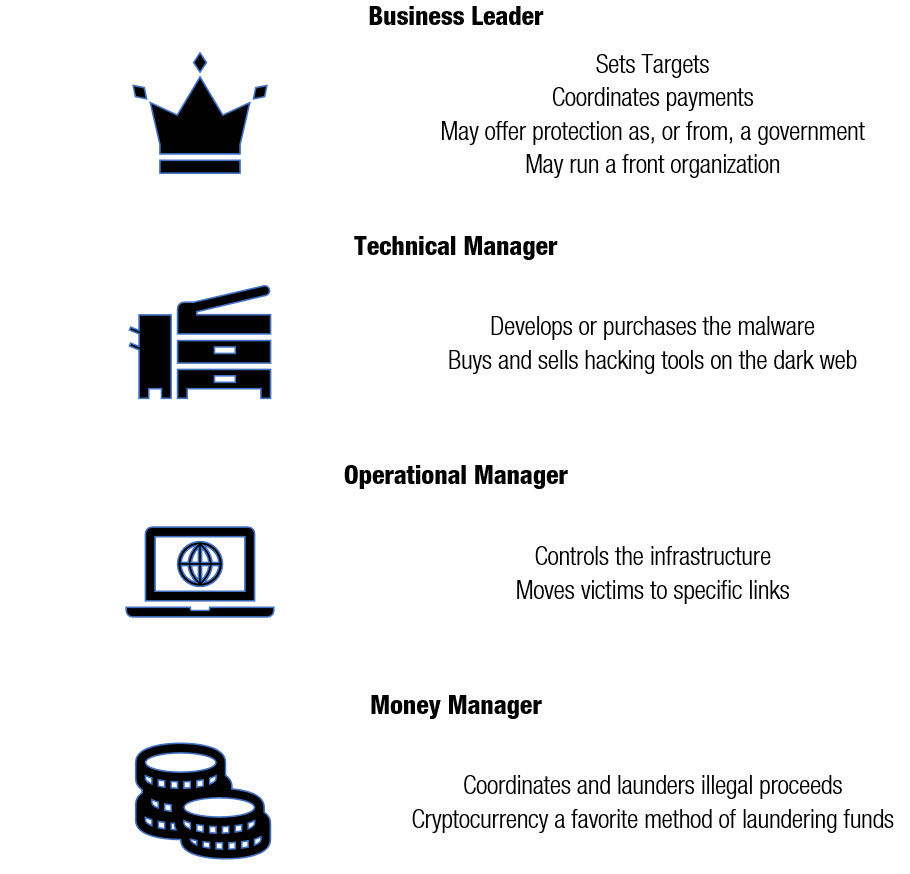
Who’s running the operation?
The top of the business is organized by either government-sponsored activity, or by overlap with other criminal syndicates. The top of a cybercriminal organization is responsible for organizing the technical, operational, and money managers. Heads of cybercriminal organization define targets and ensure money flows to the gang members. They may also be involved in setting up legitimate front businesses. For example, the Department of Justice has accused the cybercriminal organization FIN7 of running Combi Security, a firm claiming a mission “ … to ensure the security of your activities, minimize the risks of using information technology. Every appeal to us for help is considered with the utmost thoroughness on an individual basis, offering an optimal solution within the framework of the tasks set and the specific needs expressed.”
Combi Security claimed offices in Moscow in Russia, Odessa in Ukraine, and Haifa in Israel. According to a Justice Department indictment, Combi Security “ … recruited individuals with computer programming skills, falsely claiming that the prospective employees would be engaged in legitimate pen-testing of client computer networks. In truth and in fact, as Defendant and his FIN7 co-conspirators well knew, Combi Security was a front company used to hire and deploy hackers who were given tasks in furtherance of the FIN7 conspiracy.”
The worker bees
Technical Managers oversee the malware coding programmers, exploit kit authors, and crypters (where the malware software is undetectable to anti-malware software). These malware programs are not just used to attack the cybercrime victims but are also bought and sold on the black market. In the 2017 indictment against Alexandre Cazes and the dark web market AlphaBay, the Justice Department noted “AlphaBay took a percentage of the purchase price as a commission on the illegal transactions conducted through its website. ALEXANDRE CAZES, aka “ALPHA02,” aka “ADMIN,” and other operators and employees of the site, controlled and profited from those commissions, which were worth at least tens of millions of dollars.”
Operations Managers are responsible for developing infrastructure for the criminal operation. This includes making sure the hosting servers are robust and can handle mass email services and moving victims to a specific link (via email spam or hacked websites with redirect). According to the Justice Department, an example of this was the Michael Persaud case. Law enforcement alleged “ … Persaud used a California company called Impact Media LLC and other aliases to send spam on behalf of sellers of various goods and services, the indictment states. Persaud earned commissions for each sale generated by the spam …”.
Blockchain has become the preferred laundering method of cybercriminals
Finally, every criminal organization needs a way to convert foreign currency to useable money. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are very much the preferred method of laundering illegal and stolen funds. According to NullTX, cryptocurrency is perfect for illegal organization. Bitcoins, for example, offer anonymous, confidential internet use with encrypted data. There is no effective way to determine that the Bitcoin and other cryptocurrency came from illicit means such as ransomware extortion. New markets appear all the time when illicit ones are shut down by law enforcement. In some cases, cybercriminals use money mules, especially young people who are opening new accounts. Cybercriminals use mule accounts to deposit money and then transfer it to other accounts.
The sophistication and success of these organizations means cyber defense professionals will continue to have their hands full protecting their institutions from attack. Check out another RSA article, “Phishing is Still King of All Scams,” to learn more on how to protect your organization from these cybercriminals.